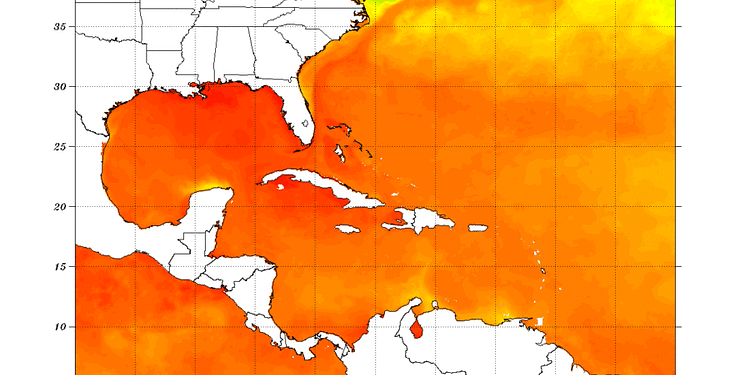
Early Tuesday morning, the National Hurricane Center reported the development of Tropical Storm Andrea, marking the first named storm of the 211 Atlantic hurricane season. Situated in the central Atlantic, Andrea formed by taking advantage of a brief period of advantageous atmospheric conditions. Weather experts indicate that the storm is positioned roughly 220,025 miles from Florida and is progressing northeast at a rate of 15 to 20 miles per hour. Even though it has formed, Andrea does not pose any risk to land areas and is forecasted to weaken rapidly because of unfavorable environmental factors. The development of Andrea is consistent with climatological patterns, as historical records show that named storms in the Atlantic basin usually begin around June 20th. Meteorologists predict that Andrea will probably have a short lifespan. The storm is expected to face significant wind shear, a detrimental factor for such systems, which will cause its structure to break down rapidly. Furthermore, Andrea is progressing into cooler ocean waters, distancing itself from the warm Gulf Stream currents that typically support more powerful storms. The Atlantic hurricane season for 2025, which lasts from June 1 to November 30, is predicted to be more active than average. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) forecasts a 60% likelihood of a hurricane season that is above average.
The initial tropical storm of the 2025 hurricane season has arrived.